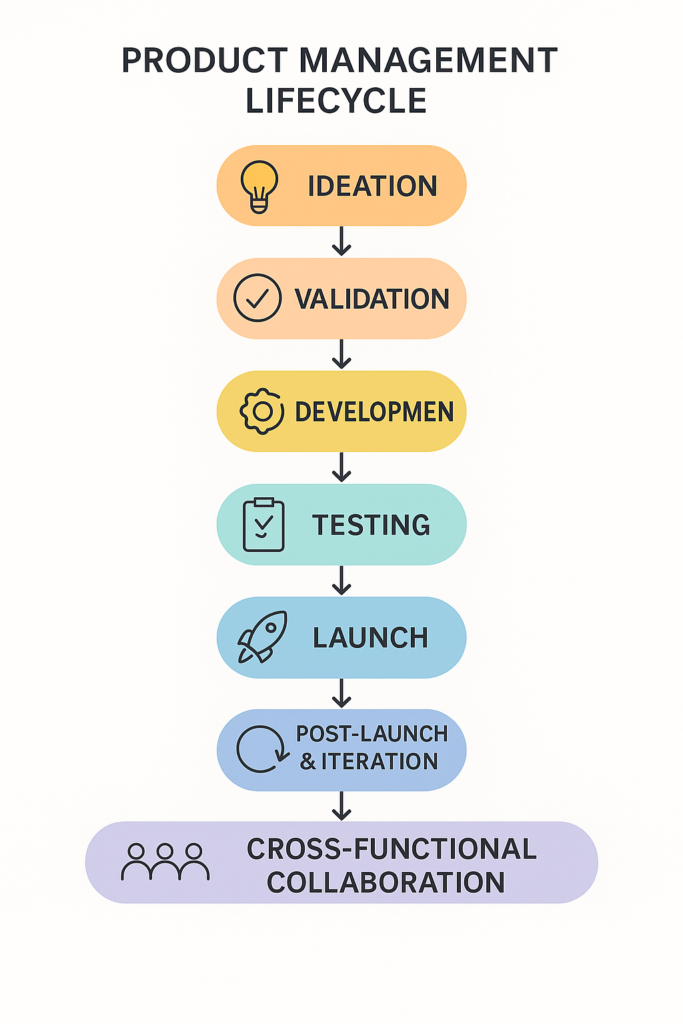
Understanding the complexities of the product management lifecycle is mandatory for turning raw ideas into successful, market-ready products. Mastering these stages can give you a competitive edge in a rapidly growing market. No matter if you’re a seasoned product manager, industrialist, or manufacturing leader.
This guide breaks down each of the seven stages of the product lifecycle management, showing how to conquer each with clarity, efficiency, and confidence.
The Importance of Cross-Functional Collaboration
One often overlooked but absolutely vital component of the product management lifecycle is cross-functional collaboration. Successful product management doesn’t happen in silos. It requires tight alignment between product managers, engineering teams, designers, marketers, and customer success units.
Why it matters:
- Enhances speed and agility by minimizing back-and-forth between departments
- Improves product-market fit through shared insights and customer-facing perspectives
- Reduces risk of miscommunication that often leads to costly delays or feature mismatches
By fostering a collaborative culture, organizations can bridge knowledge gaps and execute on the PML with precision. Effective collaboration is the fuel that keeps the lifecycle engine running smoothly.
1. Ideation: Planting the Seed of Innovation
Every product begins as an idea. The ideation stage is where brainstorming, market analysis, and pain-point research converge to shape a concept that’s viable and needed.
Key actions:
- Conduct user research to identify real-world challenges, preferences, and gaps in the market. This includes interviews, focus groups, and behavioral analysis.
- Analyze industry and consumer trends to spot emerging needs and predict future demands. Trend mapping tools and competitor analysis are useful.
- Validate ideas early by building minimal viable products (MVPs) or concept models to test desirability.
This stage in the product management life cycle sets the tone for success—powerful ideas lead to stronger products.
Now that you’ve planted the seed, it’s time to evaluate whether it’s worth watering.
2. Validation: Separating Potential from Pipe Dreams
The validation stage ensures you’re not investing in a product no one wants. Here, teams use data and feedback to test assumptions.
Key actions:
- Create clickable prototypes or basic models that simulate user experience. Share them with a small group of potential users.
- Gather structured feedback using questionnaires, A/B testing, and small-scale trials. Understand what resonates and what doesn’t.
- Perform a feasibility study to evaluate your technical capabilities, budget requirements, and resource allocation.
The product management cycle gains momentum here. This is where dreams start turning into direction.
With proof of concept in hand, you’re ready to plan the journey ahead.
3. Strategy: Laying the Roadmap to Market
Strategy defines how the product fits within the company’s mission and marketplace. At this stage, setting clear goals and KPIs is vital.
Key actions:
- Define target audiences by developing detailed personas, mapping customer journeys, and pinpointing pain points.
- Create a product roadmap that outlines features, deadlines, milestones, and responsibilities. Use project management tools to enhance visibility.
- Align your product goals with overall business goals, ensuring buy-in from executives, marketing, and sales teams.
This is where the product management lifecycle transitions from theory to structure—a bridge between vision and execution.
With your roadmap laid out, it’s time to build the engine that drives your idea forward.
4. Development: Engineering the Solution
The development stage is where your idea comes to life. Teams work cross-functionally to turn concepts into working products.
Key actions:
- Collaborate seamlessly with UI/UX designers, developers, engineers, and quality assurance specialists to build features according to the roadmap.
- Adopt agile or SCRUM methodologies for faster iterations, regular check-ins, and quicker pivots when needed.
- Set up regular feedback cycles where internal teams test the builds and share improvements for enhanced user experience.
Execution is everything here. The product management lifecycle relies on seamless collaboration to avoid delays and meet quality expectations.
With a tangible product in your hands, you’re ready to test its real-world performance.
5. Testing: Ensuring Excellence Before Exposure
Before launching, your product must pass strong quality checks. Testing ensures the product is functional, intuitive, and market-ready.
Key actions:
- Conduct usability tests with real users to uncover bugs, confusing flows, or missing features. Capture their behaviors and reactions.
- Perform performance testing to ensure your product can handle user load and operate efficiently under different conditions.
- Ensure legal and regulatory compliance, especially in industries like manufacturing, health, or finance, where standards must be met.
This phase in the product management lifecycle protects your brand and builds customer trust.
Once tested and polished, your product is ready for its grand debut.
6. Launch: Delivering Value to the Market
The launch is the high-stakes moment where strategy and execution collide. A well-executed launch can generate buzz and boost early adoption.
Key actions:
- Coordinate cross-functional teams to ensure marketing, customer support, and operations are ready to roll out.
- Develop a go-to-market (GTM) strategy that includes PR campaigns, influencer outreach, onboarding tutorials, and more.
- Track early-stage performance metrics, such as activation rates, usage, feedback, and customer acquisition costs.
This stage of the product management lifecycle can make or break momentum. Timing, messaging, and preparedness are everything.
But launching isn’t the end—it’s the beginning of a new chapter: evolution.
[We can add an image of each stage under each section.]
7. Post-Launch & Iteration: Evolving for Continued Success
No product is perfect at launch. Continuous iteration ensures the product remains relevant, competitive, and beloved by users.
Key actions:
- Collect continuous feedback through NPS scores, reviews, social listening, and support tickets to identify gaps and new opportunities.
- Track behavioral analytics to understand how users interact with your product, where they drop off, and what delights them.
- Update frequently and strategically, rolling out new features, improvements, and bug fixes that directly respond to user demands.
The final stage of the product management lifecycle is all about longevity. Products that evolve intelligently remain market leaders.
As the cycle restarts, you’re not just launching another product, you’re launching smarter.
Mapping Success with a Proven Framework
If you understand the product management life cycle stages, it will give you a blueprint to move confidently from idea to impact. By applying a repeatable and strategic product management lifecycle framework, you can align teams, mitigate risks, and speed up innovation. The true advantage lies in using a process that not only delivers results but also evolves with your business.
By having proper skill in the product management lifecycle, you can gain a strategic advantage over competitors. It also empowers teams to innovate confidently and reduce risks.
Every stage, from ideation to iteration, holds the key to success. Treat each with care, and you’ll transform fleeting ideas into long-term market triumphs.